Top 3 Recommended Policies

As the global energy landscape shifts towards renewable sources, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) have become a cornerstone technology. These systems enable efficient storage and management of energy from intermittent sources like solar and wind, ensuring reliability and grid stability. However, with innovation comes new challenges, particularly in managing the risks associated with BESS installations. Insurance tailored to these systems is emerging as a critical component for stakeholders looking to protect their investments and operations.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore everything you need to know about BESS insurance—from the unique risks involved to recent industry trends and expert insights. Whether you are an energy developer, investor, or insurer, understanding the nuances of BESS insurance is essential in today’s rapidly evolving energy market. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy’s funding to the Interstate Renewable Energy Council (IREC) underscores the growing focus on stand-alone energy storage and solar-plus-storage interconnection, highlighting the importance of risk management in this sector.
Understanding Battery Energy Storage Systems and Their Risks
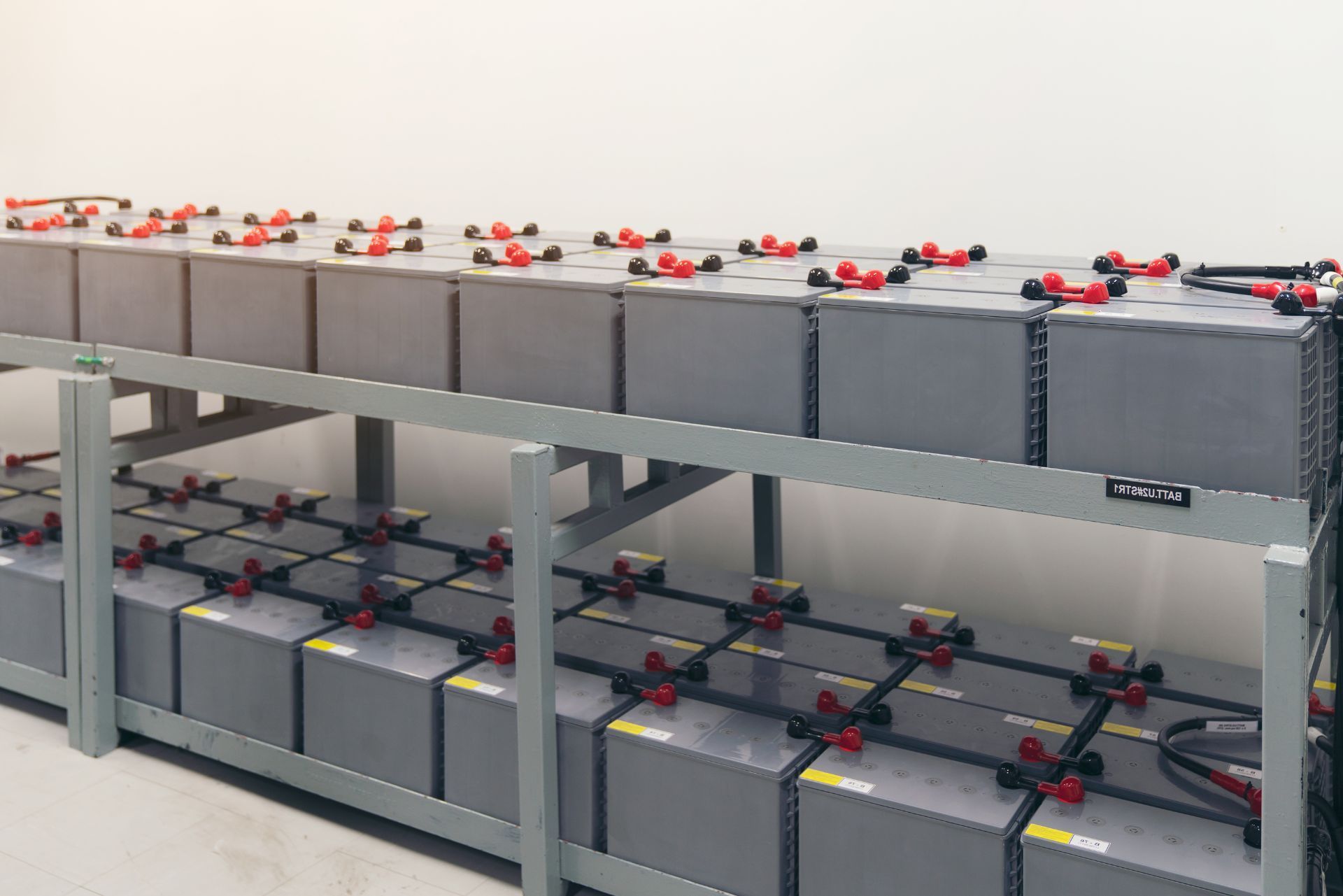
Battery Energy Storage Systems are designed to store electrical energy for later use, providing flexibility and resilience to the power grid. They are particularly valuable in integrating renewable energy sources, which are inherently variable. However, BESS technology comes with specific risks that insurers and operators must carefully consider.
One of the most significant vulnerabilities is equipment breakdown. As Greg McRae, AVP Claim, Boiler & Machinery at Travelers, points out, “The Achilles' heel of battery storage is equipment breakdown.” Failures can lead to costly downtime, repairs, or even catastrophic incidents such as fires or explosions. Regular inspections and maintenance are therefore crucial to mitigate these risks, helping to extend equipment lifespan and maximize return on investment. Moreover, understanding the lifecycle of battery components can inform better maintenance schedules and replacement strategies, ultimately enhancing system reliability and performance.
Additionally, the increasing digitization and connectivity of BESS introduce cyber risks. As these systems become more integrated with smart grid technologies, they become potential targets for cyberattacks, which can disrupt operations or cause financial losses. This evolving risk landscape necessitates specialized insurance products that address both physical and cyber threats. Companies are now investing in advanced cybersecurity measures, including real-time monitoring and threat detection systems, to safeguard their infrastructure against potential breaches. Training personnel to recognize and respond to cyber threats is equally important, as human error can often be a weak link in the security chain.
Key Risk Factors in BESS
- Equipment Failure: Battery degradation, inverter malfunctions, and thermal runaway are common technical risks.
- Fire and Safety Hazards: Lithium-ion batteries, widely used in BESS, pose fire risks if not properly managed.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Increased connectivity exposes systems to hacking and data breaches.
- Operational Variability: Load fluctuations can impact system performance and costs.
Moreover, the environmental impact of battery production and disposal cannot be overlooked. The extraction of materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel raises concerns about sustainability and ecological damage. As the demand for batteries grows, so does the scrutiny on how these materials are sourced and processed. Companies are increasingly looking into recycling programs and alternative battery technologies that minimize environmental footprints. This shift not only addresses regulatory pressures but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable practices in energy production and consumption.
Finally, regulatory frameworks surrounding BESS are continuously evolving, which can create uncertainty for operators and investors. Different regions may have varying standards for safety, performance, and environmental impact, making compliance a complex challenge. Engaging with policymakers and industry groups can help stakeholders stay informed about upcoming changes and advocate for regulations that support the growth of safe and efficient battery storage solutions. As the market matures, the development of standardized practices will likely play a crucial role in fostering confidence among investors and consumers alike.

The Role of Insurance in Managing BESS Risks
Insurance for Battery Energy Storage Systems plays a pivotal role in managing the financial impact of these risks. Traditional property and casualty insurance may not fully cover the unique challenges posed by BESS, prompting the development of specialized insurance products tailored to this sector.
One emerging trend is the integration of cyber insurance within BESS coverage. As highlighted in the Energy Storage Insurance Underwriting Market Research Report 2033, cyber insurance is becoming a pivotal component due to the increasing digitization and connectivity of storage systems. This coverage helps mitigate losses from cyberattacks, including operational disruptions and data breaches.
Moreover, insurance policies often include provisions for equipment breakdown, business interruption, and liability coverage. Given the high capital investment in BESS projects, protecting against unexpected downtime or damage is essential for maintaining financial stability. The potential for catastrophic failures, such as thermal runaway incidents, makes it imperative for insurers to develop comprehensive risk assessment frameworks that consider both the physical and operational risks associated with battery systems.
Why Specialized BESS Insurance Matters
Unlike conventional energy assets, BESS involves complex technologies and operational dynamics. Insurers must understand battery chemistry, thermal management systems, and grid interconnection standards to accurately assess risk and price policies. This specialization ensures that coverage aligns with the actual risks faced by operators. Additionally, the rapid pace of technological advancements in energy storage, such as the shift from lithium-ion to solid-state batteries, necessitates continuous updates to insurance policies to reflect the evolving landscape.
Furthermore, as the market evolves, insurers are incorporating risk mitigation strategies, such as incentivizing regular maintenance and inspections. Greg McRae emphasizes, “Regular inspections and maintenance can help prevent breakdowns, extend the lifespan of equipment and maximize return on investment.” This proactive approach benefits both insurers and insured parties by reducing claim frequency and severity. Moreover, insurers are increasingly leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling to enhance their underwriting processes, allowing them to better understand the likelihood of various risks and tailor their offerings accordingly. This data-driven approach not only helps in pricing policies more accurately but also fosters a culture of safety and reliability within the BESS industry.
Financial Implications and Emerging Trends in BESS Insurance
The financial stakes in BESS projects are considerable, with investments spanning millions of dollars. Consequently, understanding the cost drivers and potential financial risks is critical. One notable finding from recent research is the impact of load variation on operational costs. A study titled Cyber Insurance Design for Load Variation and Load Curtailment in Distribution Grids found that load variations of up to 30% can lead to doubling the daily operational cost. This highlights the importance of insurance products that can hedge against such financial risks in dynamic grid environments.
Additionally, the rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) worldwide is driving demand for energy storage solutions. According to the International Energy Agency, there were nearly 45 million electric vehicles on the road globally in 2023, including cars, buses, and trucks. This surge in EV adoption increases the need for reliable and scalable BESS installations, further emphasizing the role of insurance in safeguarding these critical assets.
The industry is also witnessing increased collaboration between government bodies and private entities. For example, the U.S. Department of Energy’s funding to the Interstate Renewable Energy Council (IREC) aims to address challenges in stand-alone energy storage and solar-plus-storage interconnection, fostering innovation and risk management practices. Such partnerships are crucial as they not only provide financial backing but also facilitate knowledge sharing and best practices, which can significantly enhance the resilience of energy storage systems against unforeseen events.
Moreover, as the market for BESS continues to evolve, we are seeing the emergence of specialized insurance products tailored to the unique characteristics of energy storage technologies. These products often include coverage for physical damage, business interruption, and even performance guarantees, which are essential for attracting investors who may be hesitant due to perceived risks. Insurers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to assess risks more accurately, allowing for more competitive pricing and customized coverage options that align with the specific needs of BESS operators.
How Insurance Supports the Energy Transition
Insurance not only protects financial interests but also supports the broader energy transition by enabling greater confidence in deploying advanced storage technologies. By mitigating risks, insurance encourages investment and innovation, helping to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy and grid modernization. As the energy landscape shifts towards decentralized generation and increased reliance on renewable sources, the role of insurance becomes even more pivotal in ensuring that stakeholders can navigate this transformation with reduced financial exposure.
Furthermore, the integration of cyber insurance reflects an adaptive approach to emerging threats, ensuring that BESS operators are prepared for both physical and digital challenges. This comprehensive risk management framework is essential for sustaining the growth and reliability of energy storage systems. As cyber threats evolve, insurers are also developing more sophisticated models to evaluate potential vulnerabilities, thus enabling BESS operators to implement robust security measures that not only protect their assets but also enhance public trust in the energy transition. This proactive stance is vital for maintaining the momentum of innovation in the energy sector, as it reassures investors and consumers alike that the systems in place are secure and resilient against a myriad of risks.
Best Practices for BESS Owners and Operators
To maximize the benefits of BESS insurance and minimize risks, owners and operators should adopt several best practices. These strategies not only enhance safety and reliability but also improve insurability and reduce premiums.
First and foremost, implementing a rigorous maintenance and inspection program is vital. Regular checks can identify early signs of equipment wear or malfunction, preventing costly breakdowns. As Greg McRae advises, proactive upkeep is key to extending equipment life and safeguarding investments. Additionally, documenting maintenance activities can provide valuable insights into performance trends and assist in future decision-making. By maintaining detailed records, operators can also demonstrate compliance with industry standards, which can be beneficial during insurance evaluations.
Secondly, investing in cybersecurity measures is increasingly important. Protecting BESS from cyber threats requires robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and employee training. Insurers may offer better terms to operators who demonstrate strong cybersecurity protocols. Furthermore, establishing a response plan for potential cyber incidents can mitigate damage and ensure swift recovery. Regularly updating software and conducting penetration tests can also help identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Additional Recommendations
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Conduct thorough evaluations of technical, operational, and cyber risks before project deployment. This assessment should include an analysis of potential environmental impacts and community relations, as these factors can influence both operational success and insurance costs.
- Engage with Experienced Insurers: Partner with insurance providers who understand the complexities of BESS technology and market dynamics. Building a strong relationship with insurers can lead to tailored coverage options that meet specific operational needs, potentially resulting in cost savings.
- Stay Informed on Regulatory Changes: Monitor evolving standards and policies related to energy storage and grid interconnection. Being proactive in understanding these changes can help operators adjust their practices accordingly and avoid compliance-related penalties.
- Leverage Government Programs: Explore funding and support initiatives like those from the U.S. Department of Energy to enhance project viability. Many government programs offer grants or low-interest loans that can significantly offset initial capital expenditures, making it easier for operators to implement advanced technologies and improve overall system performance.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of BESS Insurance
Battery Energy Storage Systems are vital to a sustainable energy future, but they come with unique risks that require specialized insurance solutions. As the industry grows and technology advances, insurance products must evolve to address equipment breakdown, cyber threats, and operational variability.
By understanding these risks and adopting best practices, BESS owners and operators can protect their investments and contribute to a resilient, renewable-powered grid. The increasing involvement of government agencies, such as the U.S. Department of Energy’s support for IREC, alongside innovative insurance frameworks, signals a promising future for energy storage risk management.
Ultimately, effective BESS insurance is not just about mitigating losses—it’s about enabling the clean energy transition with confidence and security.
Contact Us
Phone
Location
9595 Six Pines Dr, Suite 8210, The Woodlands, TX 77380